This week marks my first week in taking a Coursera course! Two of my friends joined in Stephanie Caragos and Camille Basa. These girls are waaaay ahead of me in experience so i feel both pressured that I should be able to keep up with them but super kaduper thankful for sharing their time with me.
Why Intro to Marketing? I think it would be useful for DevCon and for the upcoming ventures Ill be involved with.
Now, for the course. Our first teacher Professor Barbara Khan from Wharton University. The topics she’ll cover would be on Marketing 101: Building Strong Brands, Strategic Marketing, Segmentation and Targetting, Brand Positioning, Brand Mantra: Elevator Pitch and Experiential Branding.
Below are my notes for our first week class.
Market is the study of a market.
A market is an exchange between two partners frequently a buyer and a seller. But it also appies in nonprofits or something not necessarily money is being transacted.
What is needed to have a marketing to exist is to have an exchange.
The Essence of Marketing is to build a very strong brand.
Two Types of Market
1. Seller’s Market
2. Buyer’s Market
Seller’s Market
Productuon: Focus on the Company
– the seller has the power
– product focused marketing
– objective is to sell as much as you can
– profitability comes from volume
– proftability is tied to marketshare
– marketshare becomes your business objective
– “inside-out”
Buyer’s Market
Marketing: Focus on Customer and Competition
– the buyer has the power
– looo at what the customer want and meet the product that meets the customers need
– “outside-in”
– profitability comes from creating value
1. premium price
2. loyalty
3. cross-selling
With Connected Community
Experience
– must focus on deeper customer experiencial value (experience)
– starts before the transaction and goes after the transaction
With Economic Uncertainty
Trust
– focus on genuine customer value – RESET, discipline, flexibility
STRATEGIC MARKETING
Market-Driven Principles
1. Know your Market
2. Customers have the final say
Bundles in Decision Making
– Operations (Cost, Delivery, etc)
– Features (attributes, style, innovation)
– Customized to meet my needs
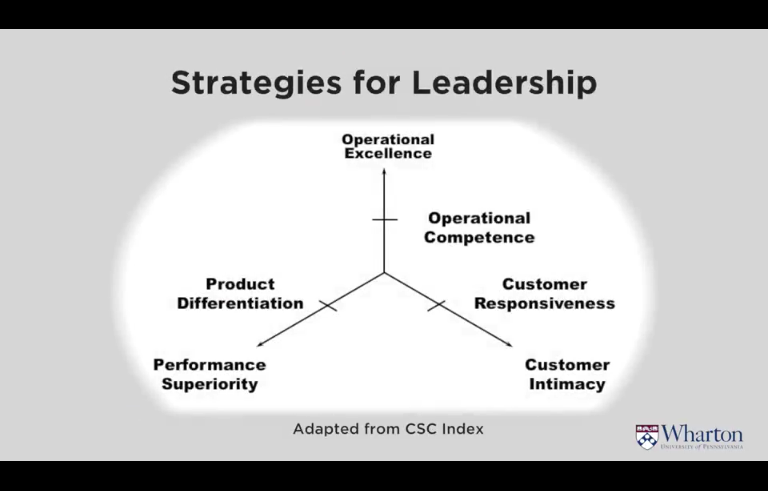
“Be best in one dimension then good enough for others”
3. Commit to being first in the market you serve
4. Deliver total quality to guarantee customer satisfaction
Fair Value
– constantly changing due to competitive reaction
Segmentation and Targetting
STP Framework
1. Segmentation
– identify variables that allow one to segment the market
2. Targeting
– evaluate the attractiveness of each segment and choose a target segment
3. Positioning
– identify positioning concepts for each target segment, select the best, and communicate it.
Segmentation Methods
1. Characteristics of the Customer
2. Benedits sought
3. Systematic, Product-related behaviours
– purchasing behavior
– by channel
Geographic Segmentation
Select a Target Segment
What makes a segment attractive?
Balancing Segment Attractiveness with our Capability
Monitor if they are matching
Segment Selection Criteria
– Segment Size
– Current Company
– Ease of Competitive entry into the segment
What is a brand?
– proprietary trademark for a specific product or service
– a contract from the company to its customers
– a promise or specific benefits, quality and value.
– a relationship
Positioning Statements
– defines the value proposition of product to the target market.
– target segment
– point of difference
– frame of reference
Points of Parity (POP)
– associations that are not unique to the brand; shared with other brands
Point of Difference
– similar to unique selling proposition
Criteria
– Are POD desirable?
– Can you deliver the POD?
Brand Mantra (Elevator Pitch)
– the way you define a brand in 30 seconds
Mental Map
– Portrays brand associations and responses for a target market. Shows how it is usually perceived.
– Ask consumers “What comes to mind when you think about ?”
– Then brand associations are grouped inyo categories.
Core Brand Values
– Set of abstract concepts or phrases that characterize the five to ten most important dimensions of the mental map brand
– relate to points-or-parity and points-of-difference
Mental Map –> Core Brand Values –> Brand Matra
Designing the Brand Mantra
1. Brand Function – describes the nature of the product/service or the type of experience of benefits the brand provides
2. Descriptive Modifier – futher clarifies its nature
3. Emotional Modifier – how exactly does provide the benedits and in what way?
Experiential Branding
Experience are processes that occur as a result of encountering, undergoing or living through situations.
Experiential Components
1. Five Senses
2. Emotions
– appeal to inner feelings
3. Cognitive
– appeal to the intellect
4. Behave
5. Social
– create feeling of community or belonging
Experience within the 4Ps
1. Product
2. Place
3. Promotion
4. Price